Components of PACS: Streamlining Image Management

Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) have revolutionized the way healthcare providers manage, interpret, and share medical images. This is because PACS is a digital solution which addresses the shortcomings and inefficiencies associated with traditional radiological procedures. To better understand the fundamental components of PACS that enhance efficiency and effectiveness in the healthcare industry, let’s explore them in more detail.
What is PACS?
The Picture Archiving and Communication System is a digital solution for the management, interpretation, and sharing of medical images. PACS transforms the traditional radiological process, providing an electronic environment that enables medical professionals to view images and conduct diagnostics easily. PACS integrates different medical imaging devices to provide an integrated platform for sharing and interpreting images.
The Components of PACS
Image Acquisition Devices
Image acquisition devices, such as CT scanners, MRI machines, DR machines, and ultrasound equipment, are essential components of the PACS workflow. These devices capture digital images, which are then converted to the DICOM format. The captured images in DICOM format are subsequently transmitted to the central PACS system for storage and retrieval. While the PACS system itself is responsible for managing and providing access to the stored images, it also integrates with other systems like EMR or RIS to ensure efficient workflow management.
PACS Server
The PACS system serves as the central digital storage location for all images captured by image acquisition devices. It allows medical professionals to access and interpret these images for accurate diagnoses. Additionally, the PACS system may provide a Guest Portal, allowing patients to view their own exams and images, enhancing patient engagement and transparency. In addition to storing images, the PACS system enables the storage and access of radiologist reports. These reports can be stored on the PACS server and accessed by authorized personnel through PACS viewing workstations or web-based viewers. This functionality, often referred to as Exam Distribution, allows for seamless integration of radiologist reports with the corresponding images, providing a comprehensive view of patient examinations.
Reading Stations
These are workstations equipped with software for image viewing and interpretation. Medical professionals use these stations to access the images stored in the PACS server for diagnostics and treatment. The software enables radiologists and other medical professionals to zoom, pan, add annotations, and adjust the contrast and brightness levels of the images.
Communication Network
Your facility’s communication networks connect all components of PACS, allowing information to be shared among different departments within a facility or between facilities. The communication network can be a wide-area network (WAN) or a local area network (LAN).
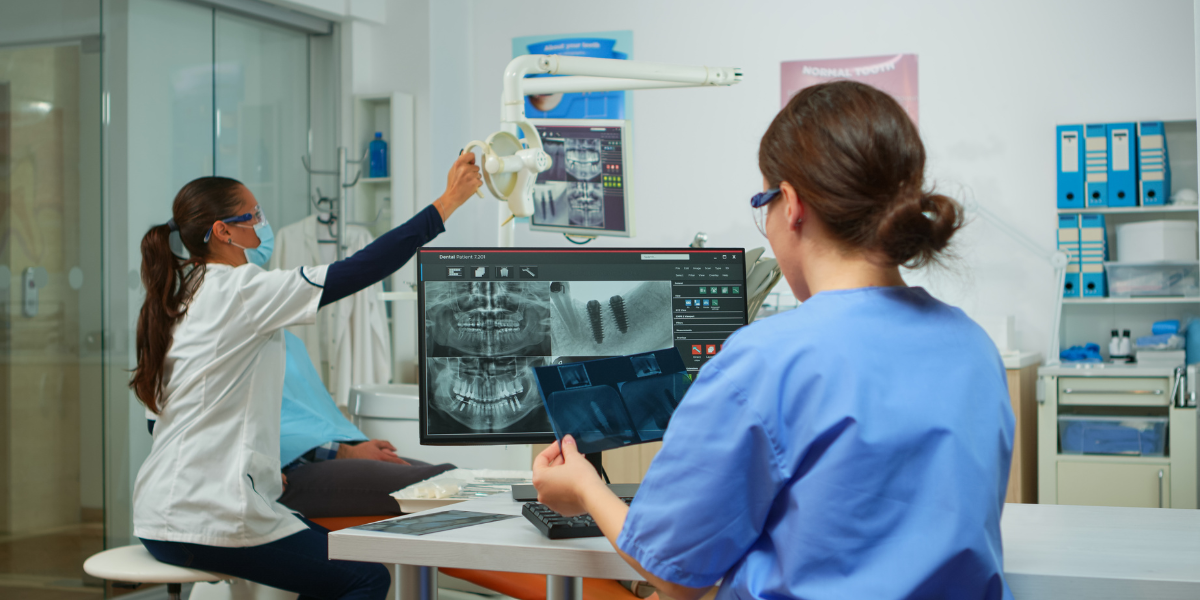
PACS serves as the central digital storage location for all images captured by image acquisition devices.
Basic Workflow of PACS
PACS workflow is a series of steps involving image acquisition, image storage, interpretation, and distribution of images:
1. Procedure Scheduling
A procedure is scheduled in the EMR, which sends the order to the PACS system.
2. Image Acquisition
Images are captured by CT scanners, MRI machines, and so on.
3. Image Transmission
The modalities transmit images to the PACS server using DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine) protocol.
4. Image Storage
Images are stored in the PACS server and organized.
5. Image Interpretation
Radiologists access the images using viewing software on their reading stations. They examine the images, make diagnoses, and store their findings inside the PACS system.
6. Reporting and Distribution
Radiologists create reports and distribute them to relevant medical professionals through the PACS system.
Benefits of PACS
PACS offers several benefits in healthcare facilities, including better workflow with acquisition and processing, improved image quality, and optimized storage utilization. By leveraging digital technology, PACS enhances overall productivity, enabling medical professionals to make more accurate diagnoses and provide improved patient care. One of the advantages of PACS is that it eliminates the need for film transportation, duplication, and storage, resulting in cost savings. Additionally, PACS systems use compression algorithms to generate smaller file sizes, making more efficient use of storage space. This efficient use of storage allows healthcare facilities to better manage their image archives and optimize storage resources. Ultimately, PACS contributes to increased patient satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and improved workflow efficiency.
Aspyra: Helping Healthcare Industries Become More Efficient
Aspyra’s PACS solution offers a comprehensive range of components that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness in healthcare facilities. By leveraging innovative digital technologies, Aspyra’s PACS solution transforms traditional radiological processes, leading to improved patient care delivery and satisfaction. Ultimately, choosing the right PACS solution is crucial to achieving operational efficiencies, cost savings, and better patient outcomes. Aspyra’s experience and expertise in PACS solutions make them a reliable provider for healthcare facilities looking to enhance their radiological processes. Contact us to learn more about PACS.